SEPTEMBER 11, 2023 | ESG, SUSTAINABILITY, ENERGY OPTIMIZATION AND MONITORING, GREEN BUILDING PRACTICES
In an era where environmental concerns have taken center stage, the imperative to adopt sustainable practices has become more pressing than ever. Commercial buildings, especially large ones like shopping malls and hotels, wield significant influence over energy consumption and environmental impact.
As the world’s focus shifts towards a greener and more responsible future, the principles of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) have emerged as guiding lights. In this blog post, we delve into the profound influence of ESG on large commercial buildings, exploring the potential for sustainability and the role of innovative companies like Tanand Technology in driving transformative change.
ESG: A New Paradigm for Business

ESG encompasses a trio of vital factors that go beyond mere profitability. Environmental factors address the impact a business has on nature, social factors reflect its engagement with society, and governance speaks to its internal ethics and policies.
The integration of these principles has gained momentum across industries, emphasizing the significance of sustainable and responsible business practices. Commercial buildings, known for their substantial energy consumption and waste generation, find themselves at a critical junction where ESG principles can reshape their impact on the planet.
The Environmental Challenge of Commercial Buildings
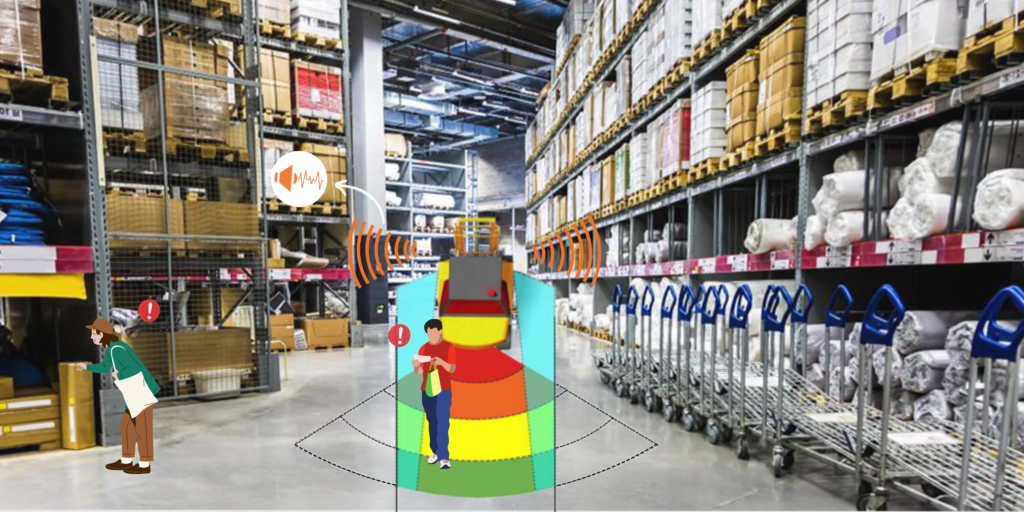
Large commercial buildings have a pronounced environmental footprint due to energy-intensive operations, high occupancy rates, and the demand for modern amenities.
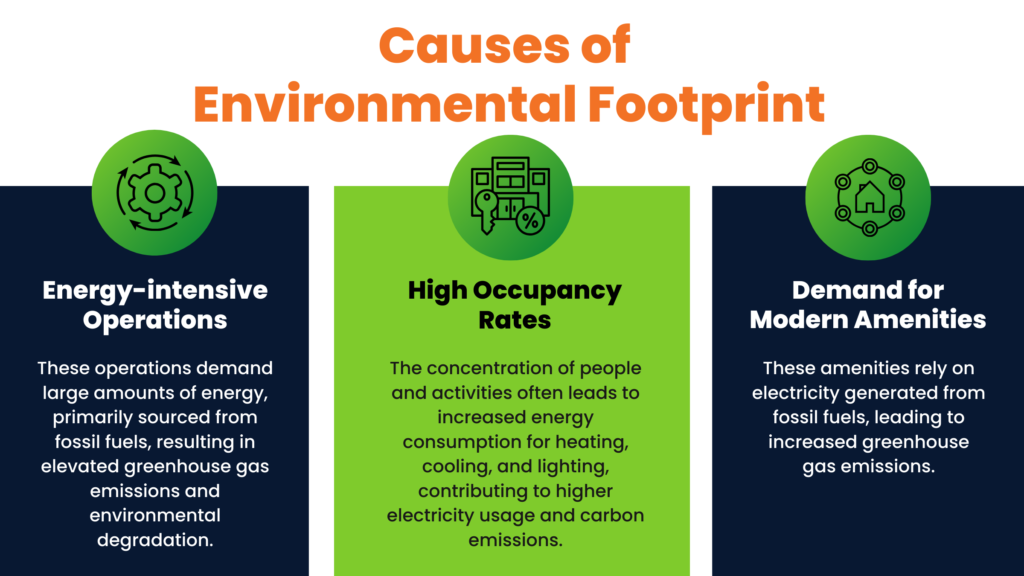
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, lighting, and electronic equipment contribute to substantial energy consumption. The resulting emissions and resource depletion underscore the urgent need for energy optimization and sustainable solutions.
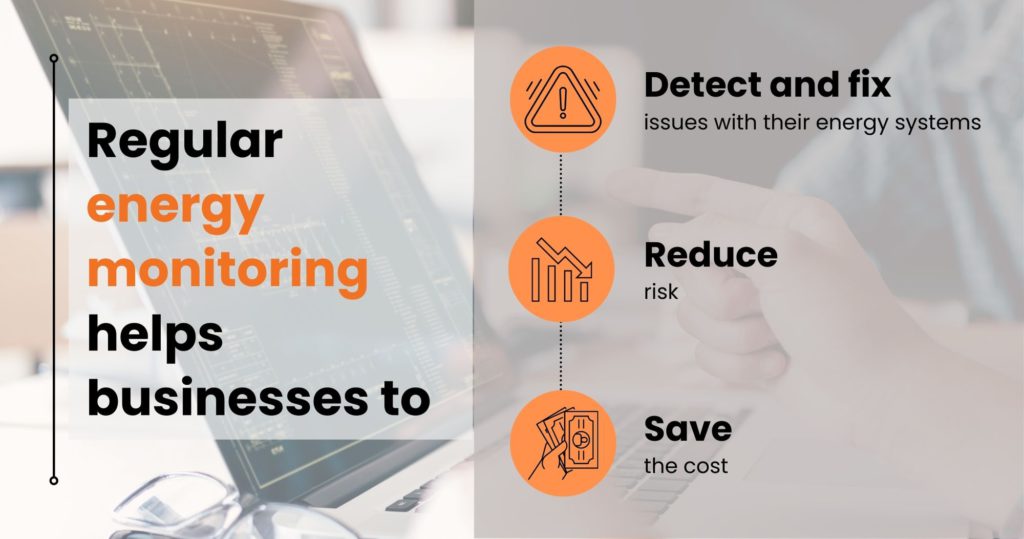
Energy Optimization: A Crucial ESG Strategy
Energy optimization is central to any ESG strategy aimed at transforming commercial buildings into environmentally conscious entities. This involves adopting technologies and practices that:
- Reduce energy consumption
- Minimize waste
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
By optimizing energy usage, commercial buildings can not only decrease their environmental footprint but also realize significant cost savings over time.
The Role of Tanand Technology: Pioneering Sustainability through Innovation
Tanand Technology, an innovative company at the forefront of HVAC energy optimization solutions. With a focus on leveraging AI-driven data analytics and real-time demand control systems, Tanand Technology offers a unique approach to ESG integration in large commercial buildings.

Our AI-driven technologies are tailored to address the complex energy dynamics of various sectors, including shopping malls, hotels, building maintenance facilities, solar systems, pharmaceutical setups, and energy-intensive food or semiconductor manufacturing sectors.
ESG-aligned Solutions by Tanand Technology
Tanand Technology’s commitment to ESG principles is evident through its suite of solutions:
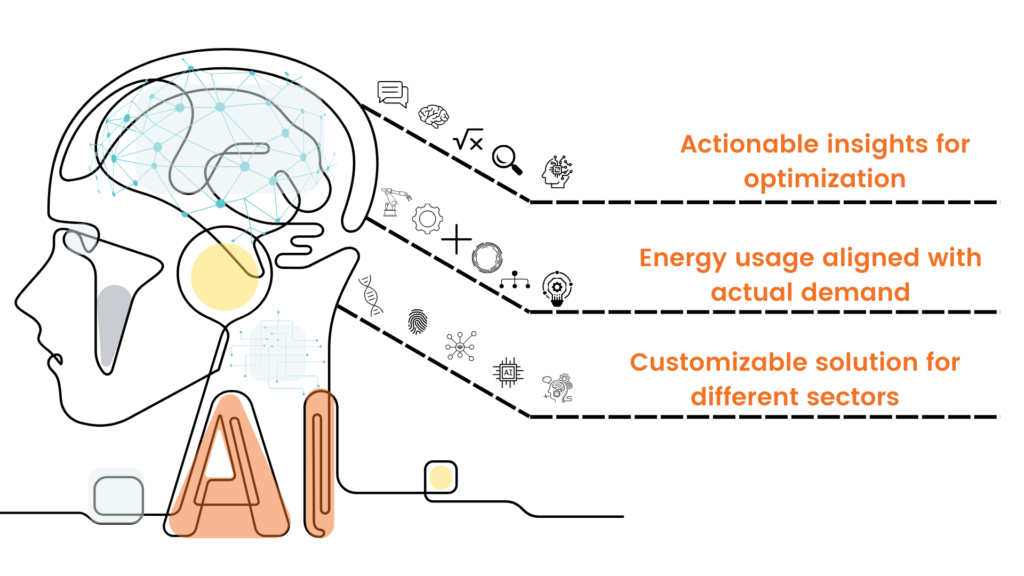
1. AI-driven Data Analytics:
By harnessing the power of AI, Tanand Technology’s data analytics platform identifies energy inefficiencies and provides actionable insights for optimization. This approach aligns seamlessly with the environmental aspect of ESG.
2. Real-time Demand Control:
The real-time demand control system ensures that energy usage remains aligned with actual demand. This not only reduces energy wastage but also contributes to responsible consumption, addressing the social dimension of ESG.
3. Sector-specific Customization:
Tanand Technology understands that each sector has unique energy consumption patterns. Their solutions are customizable to cater to the specific needs of sectors such as buildings, solar, pharmaceuticals, semiconductor and food manufacturing, demonstrating their commitment to tailored solutions in line with ESG.
ESG and the Path Forward
The adoption of ESG principles in commercial buildings isn’t just about complying with standards; it’s about embracing a new way of doing business. By integrating energy optimization solutions that align with ESG goals, commercial buildings can achieve:
- Sustainable energy saving
- Contribute to societal well-being
- Exhibit responsible governance
Tanand Technology’s role in this journey is pivotal, offering a bridge between cutting-edge technology and environmentally conscious practices.
Conclusion
The power of ESG principles lies in their potential to revolutionize the way we approach business and sustainability. Large commercial buildings, with their significant energy consumption, are ripe for transformation through energy optimization solutions.
Tanand Technology’s innovative AI-driven data analytics and real-time demand control systems embody the essence of ESG, addressing the environmental, social, and governance aspects of sustainability. As the world marches towards a greener future, these solutions offer a beacon of hope, guiding commercial buildings towards a more responsible and sustainable trajectory.
Discover more about our success stories in driving sustainability and helping clients save up to 30% on energy costs by visiting our website today.